It is Catella’s ambition to keep a dedicated and refined focus on real estate, while focusing on building a holistic approach to ESG throughout the organisation.
We believe an important step in this process is to be aware of our environmental impact and our responsibility to manage and reduce our exposure to climate-related risks within our operations and our value chain, i.e. have an understanding of how the effects of climate change may impact our organisation including our value chain in the short, medium and long term from a business and strategy perspective. The purpose of the climate risk assessment according to the TCFD framework is to gain awareness of our exposure to climate-related risks and integrate them into our overall Group risk management.
What we asked ourselves the following questions in the beginning of the TCFD process:
- How are we impacted by a changing climate?
- How do we reduce our exposure to climate related risks?
- How are we impacting the climate?
- How can we reduce our impact?
These questions developed into the more refined topics:
- The physical effects of climate change and how physical risks (e.g., extreme weather events, temperature changes and sea level rise), may impact Catella Group as well as the business areas.
- The transition to a low carbon economy and how transition risks (e.g., CO2 pricing schemes and stricter climate-related requirements) may impact Catella Group as well as the business areas.
- The development of climate risks over time in two different climate scenarios.
- Catella Group’s possibility to seize business opportunities related to climate change mitigation and adaptation.
- The initial step for assessing the criteria for climate change adaptation put forth in the EU Taxonomy.
- Understanding of which current and future financial implications the effect of climate change may have on companies.
Effects of Climate Change
The effects of climate change are interlinked, meaning that different climate effects contribute to several climate hazards. For example, greenhouse gas emissions impact the climate system and the frequency of extreme weather events such as heavy precipitation and droughts. This, in turn, increases the risk of flooding and heat stress which could lead to infrastructure damages.
The figure illustrates the relationship between drivers of climate change and its effects on the climate system, and consequently, how these changes impact nature, eco-systems and society.
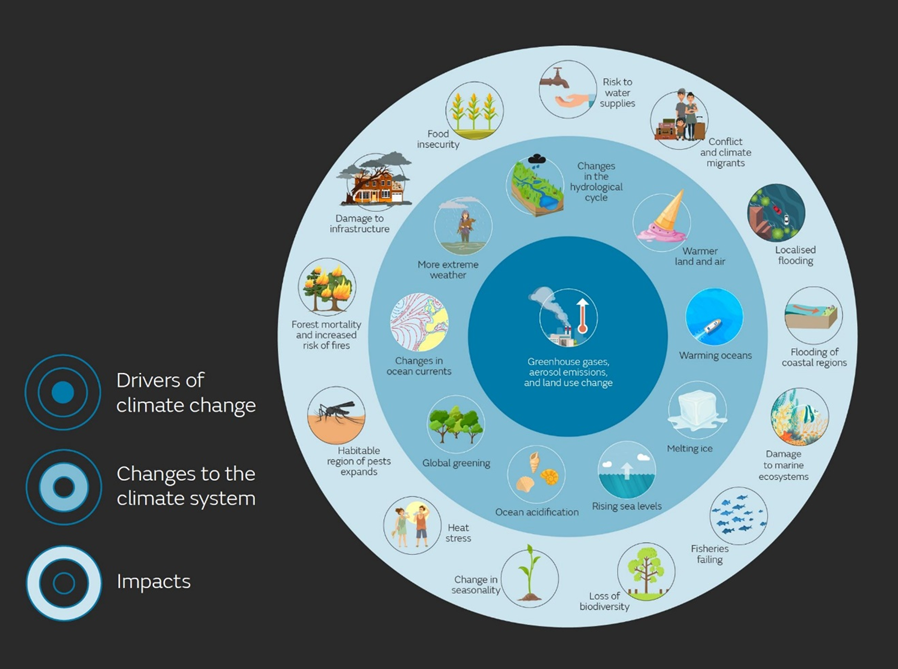
Source: Effects of climate change - Met Office
Identified climate-related risks and opportunities
Identified climate-related risks have been divided in accordance with the TCFD's recommendations of physical climate risks (acute e.g. frequents extreme weather events and chronic e.g., gradual changes in climate with consistent or irreversible changes such as sea level rise risks) and transitional climate risks (market risks, policy and legal risks, technological risks and reputational risks). Climate-related opportunities have been divided based on the TCFD’s classification of resource efficiency, energy source, product and services, markets, and resilience.
Possible mitigating and adapting to climate change opportunities:
- Resource efficiency, e.g., more energy-efficient buildings, reduced water usage
- Energy source, e.g., use of renewable energy, new technologies
- Products and services, e.g., development of climate adaptation solutions
- Markets, e.g., access to new markets, use of public-sector incentives
- Resilience, e.g., participation in renewable energy programs and adopting energy efficiency measures
Physical and transition risks
Due to different climate conditions in the regions where Catella operates, the significance of physical climate risks varies. Physical climate risks are initially highest in Western Europe, and in general lower in Northern Europe, compared to the other regions. Catella’s operations are located within Europe and the majority are within the EU region and consequently, due to similar political environment and frameworks, the actions to increase the transition to a low-carbon economy will impact Catella on all markets, implying that transition risks are higher compared to physical climate risks.
Implications of top transition risks
Within the short-term, transition risks are more likely to occur and cause financial implications on Catella's operations and value chain compared to the physical risks. We identified, increased or volatile prices, asset stranding and unreliable electric grid capacity as well as access to energy as the most significant transitional and recurring risks in all markets where Catella operates.
Summary of possible implications – climate risk assessment
The results from the climate risk assessment show that transitional climate risks, primarily market, regulatory and technological risks, are material in all regions where Catella operates in a short to medium-term perspective. This is primarily due to Catella’s broad market presence in Europe as well as European governments’ close collaborations and common regulatory frameworks. European governments often establish similar climate-related policies and action plans, including market-driven incentives to mitigate climate change and increase the transition to a low-carbon economy.
The significance of physical climate risks, both acute and chronic, varies between the markets where Catella operates. This is primarily due to differences in climate conditions in different regions of Europe. For example, the risk of heat waves/heat stress has become a significant physical climate risk in our markets in southern and western Europe as well as on the British Isles. This was specifically noticeable during the summer of 2022, which was the hottest summer on record. From a short-term perspective, the risk of flooding is the most recurrent acute physical climate risk in all regions where we operate.
From a short- to medium-term perspective, Catella is less exposed to chronic physical climate risks, as the progression of those risks takes longer and the possible financial damages occur in the longer term.
Our climate risk assessment indicates that none of the identified climate risks jeopardises Catella’s overall business continuity. However, the climate risk assessment and the scenario analysis show that the risks of climate change could have financial implications for Catella, as for all our peers. We are aware of that investing in climate adaptation measures will be necessary to remain resilient to future chronic risks.
Summary of possible implications – climate opportunity assessment
Apart from the risks associated with the effects of climate change, Catella has also identified business opportunities in the short to medium term, related to climate change mitigation and adaptation for our business, strategy and financial planning.
Catella’s business areas Principal Investments and subsidiaries in Investment Management have the possibility to seize business opportunities related to resource usage, energy efficiency and the use of energy from renewable sources in asset management, eg. brown to green conversion, and construction of new properties.
In summary, continuous integration of Group-wide climate risk assessment into current business processes, including due diligence processes, investment decisions and risk management, as well as implementing climate mitigation and adaptation actions throughout our property portfolios, will increase our competitiveness and strengthen our market position.
